Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
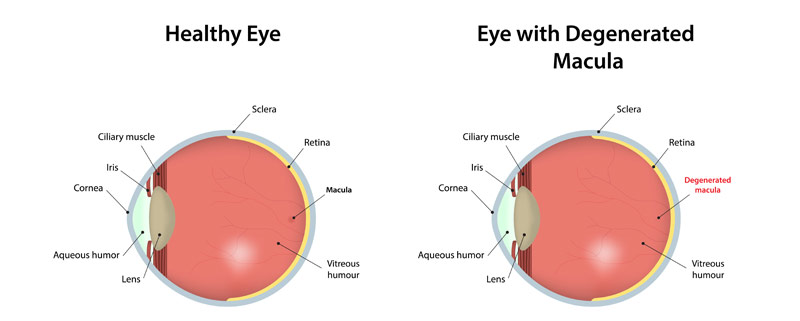
The macula is the central most part of the retina, the inner layer at the back of the eye responsible for detailed central vision. It is used for reading, driving and recognizing people’s faces. Macular degeneration is a condition that causes the center of your vision to blur while the side or peripheral vision remains unaffected. It is the leading cause of blindness in adults over the age of 55.
Who is at risk?
Some of the risk factors of macular degeneration include: family history, smoking, high blood pressure and poor nutrition. The risk of AMD increases with age. High-risk groups include smokers and people who have had extensive UV exposure. AMD is also associated with conditions such as high blood pressure, arteriosclerosis, and those with a family history of AMD.
What are the symptoms of AMD?
Symptoms of AMD may include: fuzziness of central vision, the need for increased lighting to read, distortion of objects, or the development of a central vision blind spot. The best way to detect AMD is by comprehensive eye examinations which may include advanced testing such as Digital Retinal Imaging.

Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a condition that results in the decrease or loss of central vision. It occurs in two forms, dry and wet.
Are there different forms?
- Dry AMD: Ninety percent of people who have AMD have the dry form of AMD. Dry AMD takes many years to develop, and vision may be lost gradually. Currently there is no treatment for this form of AMD. However, it is thought that very specific vitamin supplements may slow down this process.
- Wet AMD: This form occurs much less frequently but is more serious. Wet AMD occurs when new, abnormal blood vessels grow behind the retina. These blood vessels cause scarring and distorted vision by leaking fluid and blood. Treatments to exist for wet AMD, and may include laser treatments and/or certain medications.
How can I prevent AMD?
Lifelong UV protection and good nutrition are believed to play a key role in preventing AMD. Living a healthy lifestyle by keeping your blood pressure down, reducing your intake of fatty foods and not smoking are all recommended.
Is there treatment for Macular degeneration?
Currently, dry AMD is treated with ocular vitamin supplementation and lifestyle modifications such as exercise, sunglasses to reduce UV radiation and smoking cessation. Many cases of wet AMD can be treated with medications injected into the eye to stop leaking blood vessels. Early detection and prompt intervention are crucial to addressing wet AMD.

Comments closed
No comments. Leave first!